加载中
A sprained ankle can happen in a split second—whether you're playing sports, walking on uneven ground, or simply taking a wrong step. While it’s a common injury, proper care is essential to ensure full recovery and prevent long-term issues. In this guide, you’ll learn what causes ankle sprains, how to recognize the symptoms, and the best ways to treat and rehabilitate your ankle so you can get back on your feet confidently.
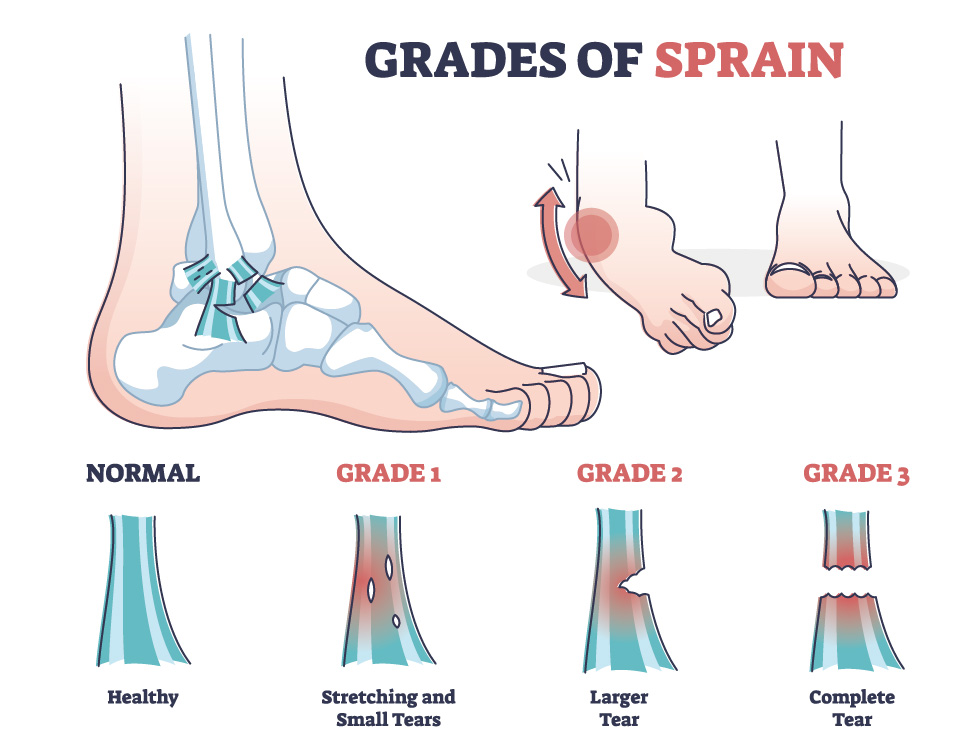
Ankle sprains are one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries characterized by damage to the ligaments surrounding the ankle joint, often caused by excessive stretching or tearing. These injuries frequently occur during activities involving sudden changes in direction, jumping, or landing on uneven surfaces. Ankle sprains range in severity from mild stretching of the ligaments (grade I) to partial tearing (grade II) or complete tearing (grade III). Approximately 90% of ankle sprains involve an inversion injury, where the foot turns inward, affecting the anterior talofibular (ATFL) and calcaneofibular (CFL) ligaments on the outside of the ankle. Less common are medial ankle sprains, resulting from an eversion injury where the foot turns outward, impacting the deltoid ligament on the inside of the ankle. Ankle sprains are highly prevalent globally, especially among athletes and those engaged in physical activities, with incidence rates ranging from 2 to 5 cases per 1000 individuals annually, primarily affecting adolescents and young adults.
The symptoms of an ankle sprain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but commonly include:
Ankle sprains are typically caused by sudden force or trauma that forces the ankle joint out of its normal position, leading to excessive stretching or tearing of the ligaments that support the joint. Some common causes of ankle sprains include:
Treatment for an ankle sprain typically involves a combination of rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and rehabilitation exercises. Here's a breakdown of the treatment approach:
Ankle braces or supports can play a crucial role in the management of ankle sprains by providing stability, support, and protection to the injured joint. Here's how ankle braces can help:
✓ Stability
Ankle braces help stabilize the ankle joint by limiting excessive movement and preventing abnormal twisting or rolling motions that could further strain the injured ligaments. This stability reduces the risk of re-injury and promotes healing of the damaged tissues.
✓ Compression
Many ankle braces provide compression around the ankle joint, which helps reduce swelling and inflammation. Compression also improves proprioception, the body's sense of joint position, which can enhance balance and coordination during movement.
✓ Immobilization
Certain types of ankle braces, such as rigid or semi-rigid braces, immobilize the ankle joint to varying degrees. Immobilization helps protect the injured ligaments from further stress and allows them to heal properly without being subjected to excessive movement or strain.
✓ Support
Ankle braces offer external support to the ankle joint, compensating for weakened or damaged ligaments. This support can enhance stability and proprioception, reducing the risk of ankle instability and providing a sense of security during activities.
✓ Pain Relief
By stabilizing and supporting the ankle joint, ankle braces can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with ankle sprains. The compression and support provided by the brace may also help reduce pain by minimizing swelling and inflammation in the injured area.
✓ Prevention of Re-Injury
Wearing an ankle brace during physical activity or sports participation can help prevent re-injury by reducing the risk of excessive ankle movement and providing additional support to the joint. This can be especially beneficial during the early stages of rehabilitation when the ankle is still healing and vulnerable to further injury.
Copy Link